India is undergoing rapid urbanisation. An ever-growing urban population necessitates an increase in urban services and infrastructure. The quality and sustainability of this urban infrastructure and services hinge fundamentally on the sound management of municipal finances, as it enables cities to plan, fund, and maintain essential services adequately.
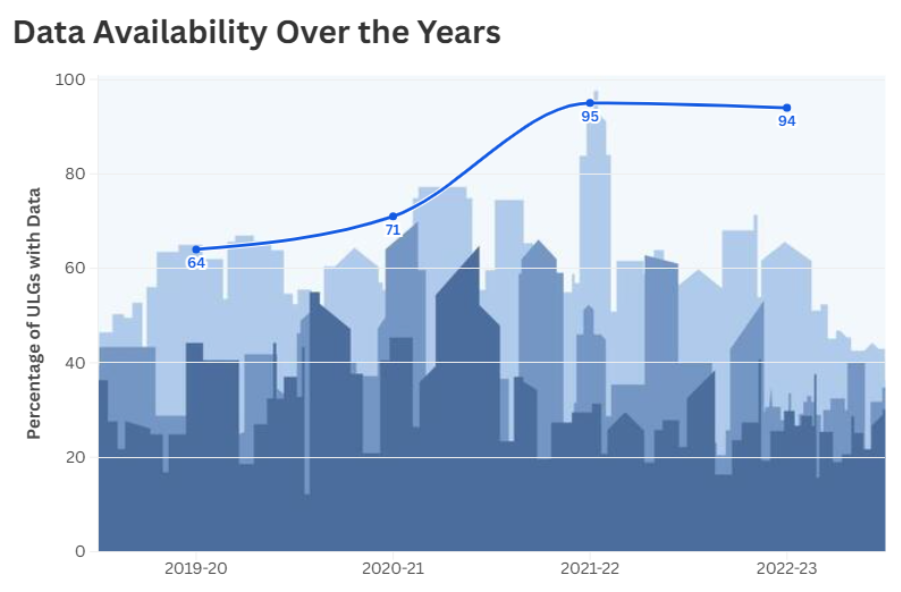
Post the 15th Finance Commission, the breakthrough that CityFinance platform has brought about in municipal finance data availability is transformative, creating new opportunities for transparency, accountability, and informed decision-making. Yet, as promising as this progress is, the journey would be far from complete without standardizing the available data.
Comparing financial data across cities becomes nearly impossible when one municipality measures revenue in one classification system while another uses an entirely different structure, much like trying to compare distances when one city reports in kilometres and another in miles, using different starting points and routes.
Standardizing municipal finance data is, therefore, the next crucial step to unlock its full potential.
From Fragmentation to Clarity: Unifying Municipal Financial Records
When municipal finance data was made publicly available on CityFinance.in, users encountered a vast but unwieldy pool of information. Data was technically accessible, yet functionally fragmented, locked behind inconsistent formats, conflicting definitions, and incompatible templates.
Significant variations remained in the reporting of municipal finance data. For example, in Tamil Nadu’s cities, data is submitted in three different formats across Municipal Corporations, Town Panchayats and Municipalities. In Odisha, cities such as Bhubaneswar, Hinjlicut, and Baripada each use varying codes and accounting structures. Similarly, cities in Punjab, across Municipal Corporations and Municipalities, do not fully adhere to the NMAM chart of accounts and codes. These variations hinder cross-city comparisons, benchmarking, and in-depth fiscal analysis, as differing terminologies, classifications, and accounting bases create opaque and inconsistent datasets.
Navigating Progress and Overcoming Hurdles in Municipal Data Alignment
Recognizing these barriers, the CityFinance platform has made significant strides toward harmonizing accounting formats and promoting the broader adoption of standardized reporting aligned with NMAM(National Municipal Accounting Manual).
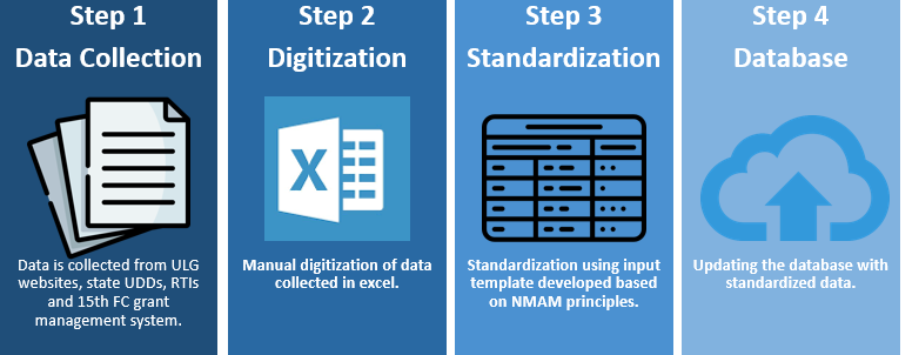
CityFinance platform’s four-step process streamlines the journey from scattered city ledgers to a unified database, making reliable municipal financial analysis accessible to all stakeholders. Following this process, the data is organized into standardized files containing 77-line items grouped under four heads – income, expenditure, assets, and liabilities – in accordance with National Municipal Accounting Framework established by MoHUA.
Through this process, substantial progress has been made: Standardized financial data for at least one year is now available for 89% of India’s ULGs on the CityFinance platform. This standardized format enables multiple analytical lenses: state-wise comparisons, temporal studies, ULG-specific assessments, cross ULG comparisons, population category-based analyses, ULG type-wise evaluations and much more.
Looking at the graph above, over 86% of ULGs with populations above 1 million have four years of standardized data from 2019–2023. This focus on larger cities has been intentional—they handle higher volumes of revenue and expenditure and serve a substantial share of India’s urban population, making their data vital for scalable insights and policy design.
The above chart highlights multiple barriers to data standardization across ULGs. These errors underscore the need for stronger guidance and technical support to improve data submission standards.
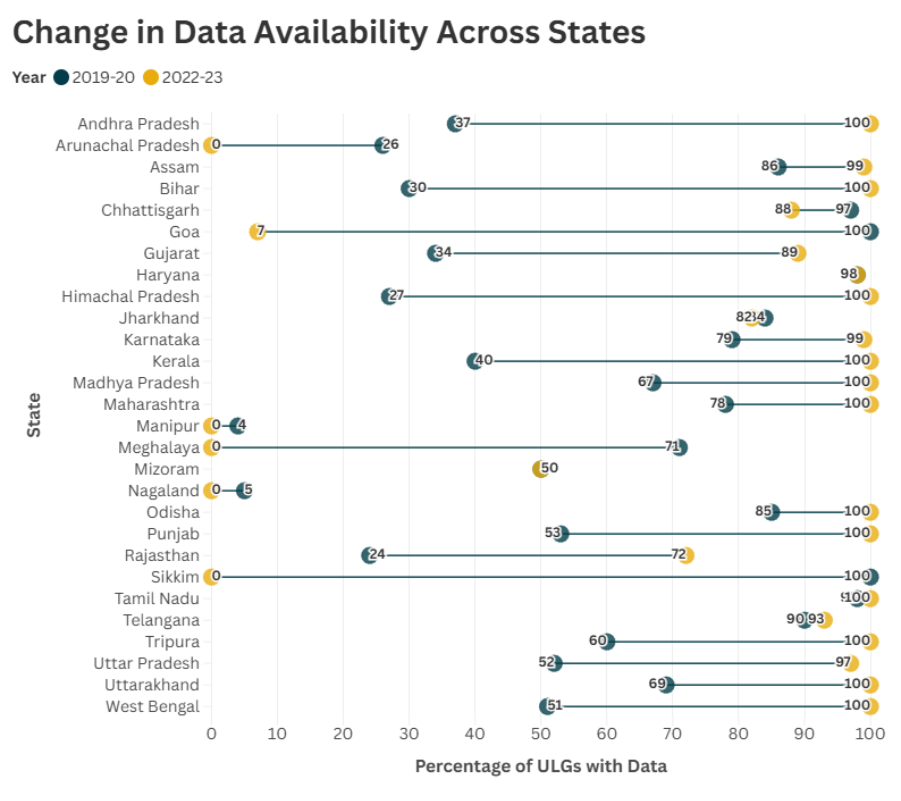
The map below reveals that over 10 states have 90% of ULGs data standardized, others, such as Haryana, Meghalaya, and Sikkim, lag significantly behind.
The Power of Clean Data: Driving Smarter Urban Governance
Standardized municipal finance data is the cornerstone of effective governance. It equips policymakers with reliable fiscal information to design targeted policies, allocate resources effectively and benchmark performance across cities.
Standardized data empowers cities to assess their financial health, monitor compliance, and improve service delivery. It enables evidence-based planning, better budgeting, and performance benchmarking across peers.
For state and national government officials, standardized municipal finance data provides a reliable basis for monitoring fiscal performance, designing incentive frameworks, and targeting capacity-building efforts. It enables cross-ULG benchmarking, compliance tracking, and policy evaluation at scale.
For market participants i.e. credit rating agencies, investors, and financial institutions – standardized data enhances visibility into municipal creditworthiness, enabling risk assessment, debt structuring, and investment in instruments like municipal bonds with greater confidence.
Standardized municipal finance data offers researchers and civic organizations a consistent, comparable foundation to analyze urban fiscal trends, governance outcomes, and equity in resource allocation. Civil society groups can use this data to monitor public spending, engage constructively with local governments, and push for reforms grounded in evidence and public interest.
Breaking Barriers: Building a Resilient Municipal Finance Data Ecosystem
Standardized municipal finance data has begun to reshape urban fiscal governance, enabling smarter policy, better financial management, and more informed understanding.
However, this is just the beginning. The next frontier lies in tapping directly into ULG systems to automate data exchange and eliminate manual reporting and duplication. Integrating technologies like APIs and accessing centralized accounting systems can ensure seamless, timely, and accurate data flows. Alongside this, targeted capacity-building for municipal officials and stronger enforcement of reporting standards will be critical to sustaining data quality and expanding coverage. CityFinance is actively working to enable this shift.
To dive deep into the standardization process, see: How We Standardize Annual Financial Statements? Explore standardized municipal finance data on CityFinance and see how your city compares.